Is it possible to reveal the truth without necessarily sharing secret information? Welcome to the world of Zero-Knowledge proofs! A technology born in the 80s, Zero Knowledge proofs have recently been redefining the blockchain space. But what is zero knowledge? How does it work? Well, keep reading our guide.
What is Zero Knowledge?
Zero-knowledge refers to a technological concept where parties to a deal can prove the existence of the agreement or transaction without necessarily sharing the actual details.
These proofs were first coined in 1985 when a group of 3 experts named Charles Rackoff, Shafi Goldwasser, and Silvio Micali released the paper “The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof-Systems.“
Although born nearly 40 years ago, Zero-knowledge proofs have been gaining usage within the technological universe over recent years.
The blockchain world demands that the prover prove the legitimacy of a transaction completed between two parties.
But, with the power of ZKPs, the prover can prove to the verifier that they know a specific piece of info without necessarily sharing it. This brings a secure process of authenticating transactions within the cryptography realm.
How Do Zero Knowledge Proofs Work?
Earlier, we mentioned the presence of at least two parties in a ZKP system: the prover and the verifier.
The prover has some private and highly confidential information. It’s the prover’s responsibility to prove to the verifier that they possess this info. The verifier has only one job: verifying that the prover has the information.
In the very initial step, the prover and verifier set up and agree to specific parameters and cryptographic algorithms applicable in the process. The prover follows by generating a cryptographic statement of commitment — a proof without the details of the statement.
The verifier then issues a random challenge to the prover. As such, the prover must generate a response based on the challenge and the commitment. Finally, the verifier checks the response, compared with the original challenge and commitment, to determine the validity of the prover’s statement.
Note that, in all these steps, the verifier cannot see the details of the statement. Instead, they only see the proof.
In the blockchain universe, there are two types of ZKPs. They are:
- Interactive ZKPs — These require multiple rounds of interaction between the prover and verifier.
- Non-Interactive ZKPs – Once the prover generates the proofs, there is no other interaction with the verifier. The proof created can be verified fully by anyone.
Within the blockchain universe, ZKPs have proven vital in developing a blockchain landscape with privacy and scalability.
What are the Primary Characteristics of ZKPs?
A zero-knowledge proof, be it interactive or non-interactive, must possess three of the following characteristics:
- Completeness: If a statement is true, an honest verifier can be convinced by an honest prover that they know the correct input.
- Soundness: If a statement is false, then no dishonest prover can unilaterally convince an honest verifier that they know the right input.
- Zero-knowledge: If the state is actual, then the verifier learns nothing more from the prover other than the statement is true.
Divisions of ZKPs
There has been a massive demand for ZKPs to deliver various services in the blockchain realm. As such, over the recent months, we have seen an enormous rise in projects leveraging zero-knowledge proofs.
While the concept is the same, i.e., ZKPs, multiple iterations exist. Among the iterations of ZKPs in blockchain tech are:
- ZK SNARKs
- ZK STARKs
zkSNARKS
ZKSNARKs is a unique iteration of ZKPs, which stands for ZK Succinct, Non-interactive Argument of Knowledge. First developed in a 2012 paper, the philosophy of zkSNARKs has gained immense usage in the crypto realm.
Their “SUCCINCT” nature means these ZKPs are very easy to verify in a fraction of a second.
SNARKs are Non-Interactive, meaning there is no to-and-fro engagement between the verifier and prover. These are merely short, one-way messages with complete proof of info.
zkSNARKs function through the interaction of 3 key algorithms: Key generator (G), Prover (P) and Verifier function (V).
zkSTARKs
zkSTARKs, like zkSNARKs, has the primary role of bolstering scalability. STARKs refers to ‘Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge.’
Like SNARKs, STARKs are, by design, also non-interactive proofs. However, unlike SNARKs, STARKs are designed to foster more transparency while affording services.
The functionality of STARKs differs from SNARKs. The network combines the principles of probabilistic checkable proofs (PCPs) and interactive oracle proofs (IOPs).
Crypto Projects Implementing ZKPs
Z-Cash
Built on the founding principles of blockchain, Z-cash aimed to foster utter privacy for those within the crypto realm. At its launch, Z-Cash brought the ZK SNARKs concept to bolster anonymity.
Its privacy focus has made this crypto network among the most prominent players in the crypto realm.
At the heart of ZCash is the native token ZEC, which helps provide services and secure the network. The coin is currently positioned at number 135 based on market cap rankings.
zkSync
Second in line, zkSync!
Source: zkSync
zkSync is a crypto network launched as a layer two protocol to serve the needs of Ethereum network users. It was established due to growing demand for more efficient and cheaper Ethereum transactions.
To provide top L2 services, the network uses Zero-knowledge proofs. It is among the few top ZKP networks providing L2 services for Ethereum.
zkSync saw impressive growth in 2023, especially after its mainnet launch, opening the road for DeFI, NFT and GameFi growth.
Loopring
Loopring is a platform focused on scaling decentralized exchanges. In its provision of crypto trading solutions, Loopring leverages a hybrid ZKP. In essence, order messaging happens off-chain, while settlements happen on-chain.
ImmutableX (IMX)
A key player in the universe of NFTs, ImmutableX is leveraging ZKP to streamline the trading of NFTs. Immutable X submits its proofs on the StarkNet instead of Ethereum. StarkNet then bundles all the transactions and posts the evidence of their existence to Ethereum.
Owing to the use of ZKP, Immutable X has been capable of supporting myriads of transactions with meagre fees.
Polygon (MATIC)
In recent years, ZK rollups have emerged as a more exciting solution for Ethereum’s scalability. Polygon has recently implemented ZK rollups on the Ethereum Virtual Machine to bolster scalability. Its new introductions, Zero, Hermez, Nightfall, Miden, zkEVM and Polygon 2.0, leverage ZKP.
Mina (MINA)
Mina Protocol boasts the capability of operating as the lightest blockchain network in the world. It capitalizes on the principle idea of a ‘succint blockchain.’
It leverages ZKPs to compress the blockchain into a tiny snapshot, easily verifiable even via mobile devices. Because of leveraging ZKPs, Mina only has a size of 22KB.
DYDX (DYDX)
Another decentralized exchange network, DYDX, uses ZK Rollups to bolster scalability. The idea is to back multiple transactions to create one single proof. This way, DYDX charges low fees while still trading at top security.
Worldcoin (WDC)
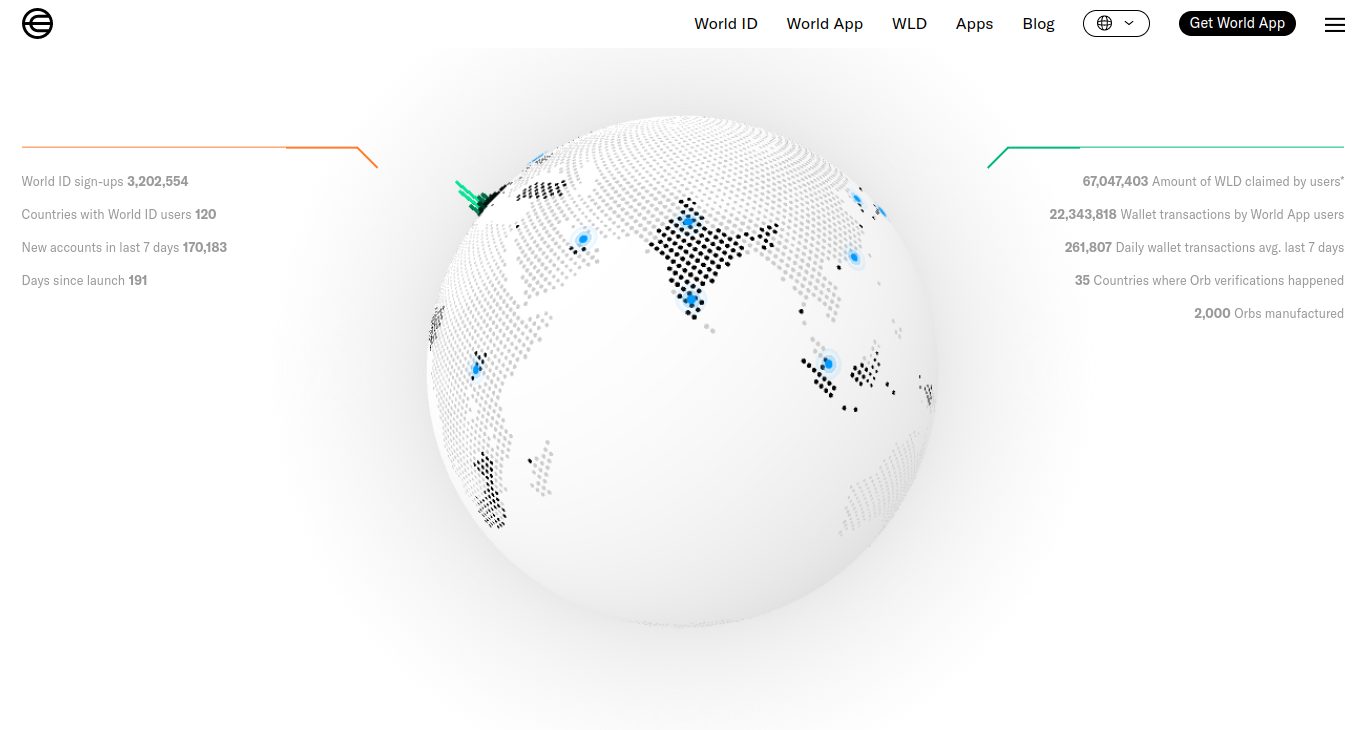
Source: Worldcoin
Popular project Worldcoin, known mainly for providing WorldIDs, leverages ZKPs to bring scalability, security and privacy to its users.
Uses of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
We have already established a massive advantage for blockchain networks using ZKPs within the crypto realm. ZKPs bring many valuable use cases and foster adoption. Among the primary use cases include:
Layer-2 Rollups
The scalability issue has damaged most older blockchain networks, including Ethereum and Bitcoin.
It’s for scalability reasons that the idea of Layer-2 scaling solutions emerged. While there are many L2 solutions, ZK rollups have been making waves in the crypto realm in recent years.
These rollups bundle thousands of transactions and publish them on the main chain. Using ZKP means validation is faster, and fees are lower in L2s. zkSync and Starknet are among the most popular rollups leveraging ZKPs.
Voting Systems
The most demanded features in a voting system, whether physical or digital, are security, verifiability and privacy. However, traditional voting systems never guarantee any such features to users.
Enter ZKPs!
ZKPs create a safe and verifiable voting system, allowing voters to cast votes without revealing their identities. The systems will never display the users’ identity or voting preferences, even in the verification.
As such, voters can confirm their vote is recorded without disclosing who they voted for.
Privacy-Preserving Transactions
While blockchain demands transparency in transactions, there is a huge demand for privacy from users. In essence, privacy leads to at least more security.
ZKPs allow users to complete transaction validation without necessarily accessing transaction data. These proofs obscure the details of the transaction amounts, participants, and even smart contract codes used.
Decentralized Identity
The demand for identity verification has been growing, especially since the emergence of blockchain. Still, privacy remains a critical demand in digital identities and DeFI applications.
You can complete decentralized identity verification without disclosing personal info with zero-knowledge proofs. The result is top privacy, without necessarily the need for passwords, which are susceptible to phishing attacks.
Internet of Things (IoT)
With billions of devices linked to the internet, there needs to be a system that protects everyone’s privacy. ZKPs can help verify that software updates are verified and that only authorized devices can access network and user data.
Does Bitcoin Need Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
Yes!
One of the biggest problems affecting the Bitcoin network in 2024 is the issue of scalability. Despite its vast user base, the network can only deal with seven transactions every second.
Hundreds of thousands of transactions are pending every second in the Bitcoin blockchain. But can ZKPs help solve that?
Well, YES!
The high transaction fees, low scalability, and low transaction processing speeds are all problems ZKPs can solve.
With the Bitcoin blockchain seeing increasing transactions because of BRC-20 and ordinals, ZKPs can be a good solution.
Even more, there have been proposals to provide ZKP-focused smart contract options in the Bitcoin network.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do ZKPs Benefit Blockchain Technology?
ZKPs enhance blockchain technology by adding layers of privacy and security, allowing transaction verification without revealing actual details. This maintains both transparency and privacy.
Can You Give Examples of Blockchain Projects That Use ZKPs?
Some blockchain projects that use ZKPs include ZCash, ZKSync, Polygon, Mina and DYDX.
What Are The Common Applications of Zero Knowledge Proofs?
ZKPs are commonly used in blockchain technology to enhance privacy, in secure voting systems to verify eligibility without revealing voters’ choices, and in authentication systems to prove identity without sharing credentials.
Are Zero Knowledge Proofs Secure?
Yes, when properly implemented, Zero Knowledge Proofs can be truly secure.




